AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D is going to release on 20th April. It comes with a unique and innovative 3D V-Cache technology which can change the future of processors.
They say CPUs are just rocks which we have tricked into thinking or processing information. Technically, that is correct. However, a huge amount of effort and technology goes into making these CPUs, to allow them to process information.
Modern day CPUs work in a very complex way. But the intentions behind them are the same as always. They process information, which is sent to them and they also need various features to operate. These features include CPU caches.
How CPU caches works
Whenever one opens a software or an app, it usually reads all the data from the storage drive and loads it temporarily into the RAM, also known as memory. The RAM is usually a stick shaped circuit with memory chips on it, inserted into the main computer circuit called the motherboard. The CPU uses lanes inside the motherboard to connect with the storage drive and the RAM, to receive, process and send information.
The problem is, connecting and transferring information between the RAM and the CPU is quite quick, but it is still is not as quick as required. This is why CPU makers use something known as CPU caches.
In CPUs, cache is like a memory chip installed directly inside the CPU. Cache works like a great medium between the CPU and the RAM. What it does is it allows the CPU to store important information inside it, which it can access very quickly without needing the CPU to make a trip to the RAM to get that information.
Cache speeds and sizes
Caches comes in various sizes and speeds, too.
The L1, that is level 1 cache, is usually the quickest and is sized at less than 100 KB per core in a modern day CPU.
The L2, that is level 2 cache, is slightly slower than the L1 cache and usually comes in less than 2 MB per core size.
The L3 cache, the slowest of all three (still faster than RAM), but also the largest, maxes out at 32 MB these days in modern day CPUs.
As one can notice. Compared to a single RAM stick, which usually come with the overall average memory size of 8 GB and 16 GB these days, the size of the CPU caches are extremely small. This is because a CPU is constrained by its size. One cannot add too many memory chips inside a small CPU due to that. It needs the processing power to process information, too. So very little room is available to put a big cache inside a CPU. This is where 3D stacking can play an important role.
3D stacking
Usually, memory chips are normally laid next to each other, connected to each other via the wiring in the circuit. It has been a standard since time known. Means it requires space and power to transfer information from one place to elsewhere. This is where 3D stacking comes.
Basically, in 3D stacking, computer chips are stacked onto each other – one on top of another. They are then connected vertically to each other with a through-silicon via (TSV), which allow these chips to have very small amount of space between each other. These special chips are usually thinner than the usual and having 8 to 16 chips stacked onto each other is not something unknown.
Doing this has many advantages. First, it takes lesser space, so it allows more powerful devices in smaller size. Second, it reduces the power usage. Third, it increases the overall speed of the stacked chips and much more.
3D stacking is a technology that is not exactly new. It has been worked upon since half a century. However, it’s only in recent decades in which we are seeing its results.
Examples of 3D stacked chips
The PlayStation Portable (PSP) by Sony was the first commercially available product to use this tech in its RAM chips made by Toshiba. Later, Toshiba also made NAND based memory chips, the ones used in SSD and microSD cards. Then DDR3 RAM chips were made with the same tech by the likes of Elpida Memory, SK Hynix, Samsung, Micron and others.
Some years later, AMD got together with Samsung and SK Hynix to make High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), which is based on similar 3D stacking technology of memory chips, for its graphics cards. The HBM2 announced later by Samsung started with a support for 8 GB per memory stack.
Samsung has used the same 3D chips technology with some of it’s newer Solid State Disk (SSD). Nowadays, many SSD makers use the same technology.
AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D
Months ago, when AMD announced 5800X3D, everyone wondered whether they would be able to pull it off. The reason is simple. It is among the first commercial consumer CPUs to be made available with the 3D V-Cache technology. The same one mentioned above.
AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D’s features are similar to that of Ryzen 7 5800X. Except it is clocked lower than 5800X and while 5800X comes with 32 MB cache, 5800X3D comes with 96 MB of L3 cache, thanks to its 3D stacking technology.
Except, AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D is priced at $449, which is the same as the original price of 5800X.
How 3D V-Cache is implemented
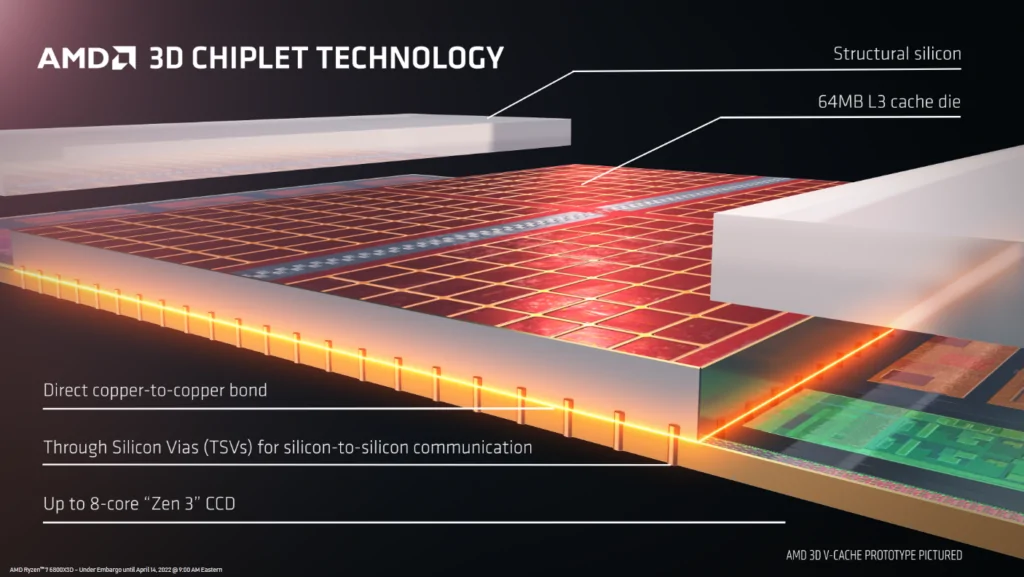
Basically what AMD has done is that it has kept the 32 MB cache as it is, but instead, installed a 64 MB cache on top of the main L3 cache, taking the total L3 cache to 96 MB on AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D. This, AMD claims, gives excellent gaming performance. Is it really so. We cannot really say for sure. Until recently when various sites got an hold on them and ran benchmark tests on 5800X3D.
AMD 5800X3D reviews and benchmarking results
Most reviews have found one thing common. AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D does not do extraordinarily when it comes to raw processing work. It is because it is clocked lower than AMD Ryzen 7 5800X to prevent overheating due to the stacking of cache chips.
However, what was impressive is its gaming performance. Take Tom’s Hardware review for example. It shows that AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D on average is beating all the CPUs currently in the market in gaming performance. This includes Intel’s most powerful CPU Core i9-12900KS, which is released recently and is priced at $739, compared to just $449 of 5800X3D.
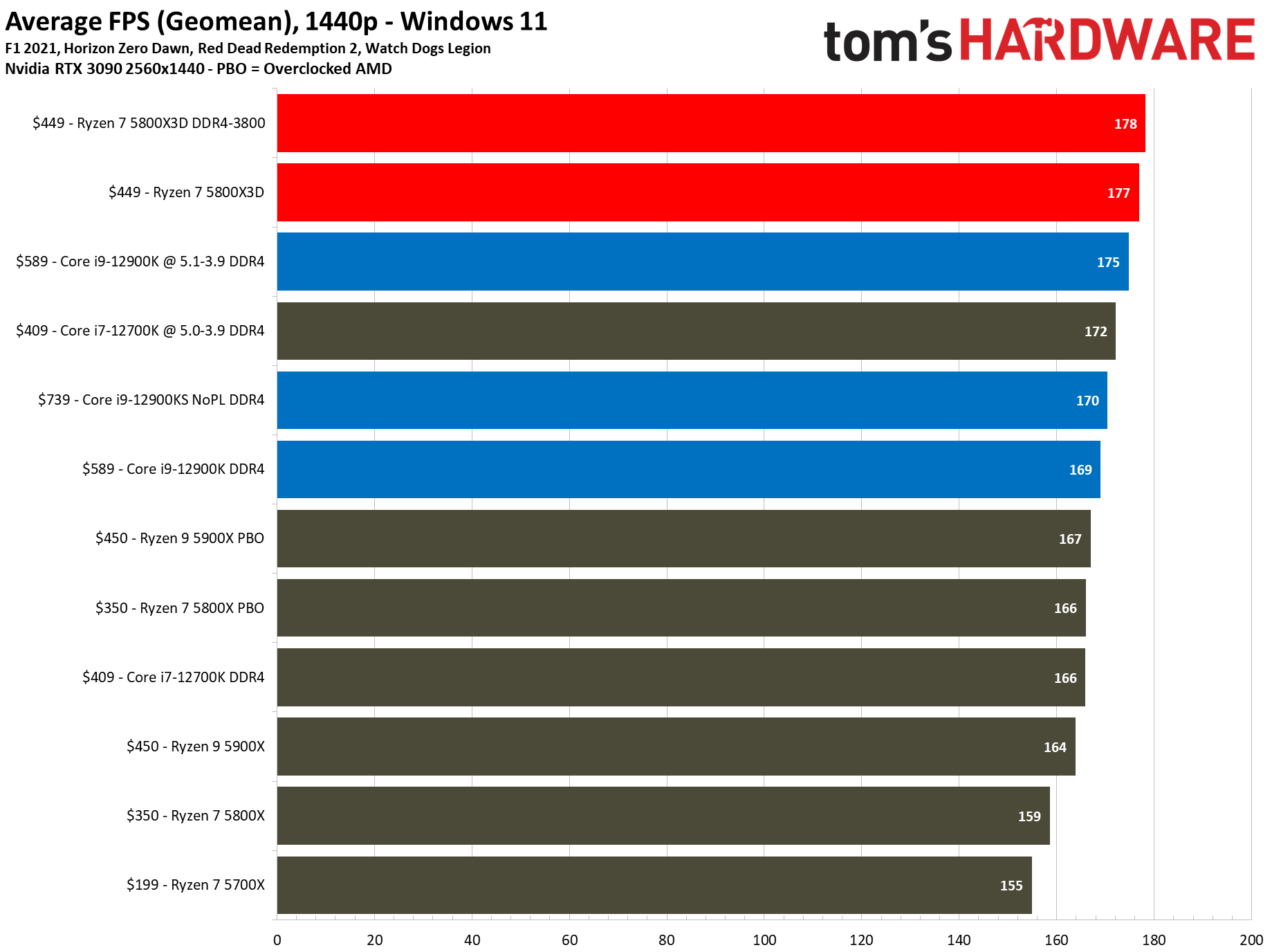
Reviews after reviews after reviews. Most of them are showing the same thing. Ryzen 7 5800X3D is the fastest in almost all the games. That too with significantly lower power usage.
Benchmarks explained
AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D being faster than other processors in gaming has a reason behind it. In gaming, a lot of textures and gaming assets are required to be loaded in the memory. Because of that, the cache plays a very important role. This why 5800X3D shines with its bigger cache of 96 MB.
The problem with some reviewers is that they want to disregard such a huge upgrade in gaming performance by comparing its speeds in the synthetic and other software based benchmarks. The truth is, most people have no real world use for such benchmarks. No one is going to buy such an expensive CPU to run synthetic, non-real world use benchmarks and certainly, most common users are not going to buy them to compress files regularly. A huge amount of expensive CPU buyers buy them for gaming performance. This is why AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D is an important and innovative entry in the market. It gives gamers an important option.
Current AMD users to benefit a lot
The important part about AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D is that it uses AM4 CPU socket, which is the same socket used in all the previous desktop Ryzen processors. This means a lot of motherboards released in the last couple of years are going to work with this processor, depending on the manufacturer support. So this can be an excellent upgrade for those already on the Ryzen platform as they only need to change / upgrade their CPU – hardware wise. 5800X3D possibly being the last CPU in the AM4 socket – Zen 4 based AMD Ryzen 7000 processors will use an entirely new CPU socket called AM5, which will be based on LGA technology and not the PGA one found in AMD processors until now.
Future of 3D cache processors
AMD has shown with it’s Ryzen 5800X3D the importance of the CPU cache. From decades, we have known that the more the CPU cache, the faster it can be in some tasks. Only problem was that the limitations in the technology available. Till now, CPU caches have kept increasing gradually. But this takes it to the next level.
If the performance gains continue with this technology. We expect or at least hope Intel to follow the suit in some of its processors. If not mainstream ones, then special gaming oriented ones. We want AMD to continue with this newer tech in many, if not all of it’s upcoming CPUs to be released by them.